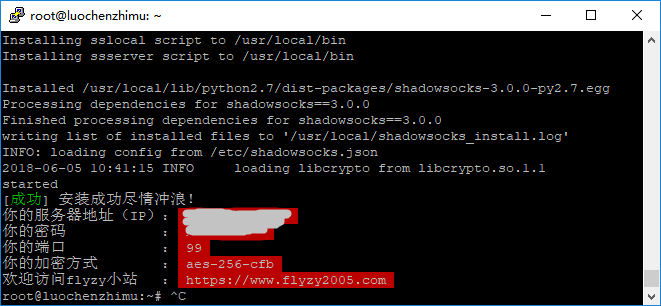
Install Goolge BBR on CentOS
CentOS安装谷歌BBR加速插件
BBR (Bottleneck Bandwidth and RTT) is a new congestion control algorithm which is contributed to the Linux kernel TCP stack by Google. With BBR in place, a Linux server can get significantly increased throughput and reduced latency for connections. Besides, it's easy to deploy BBR because this algorithm requires only updates on the sender side, not in the network or on the receiver side.
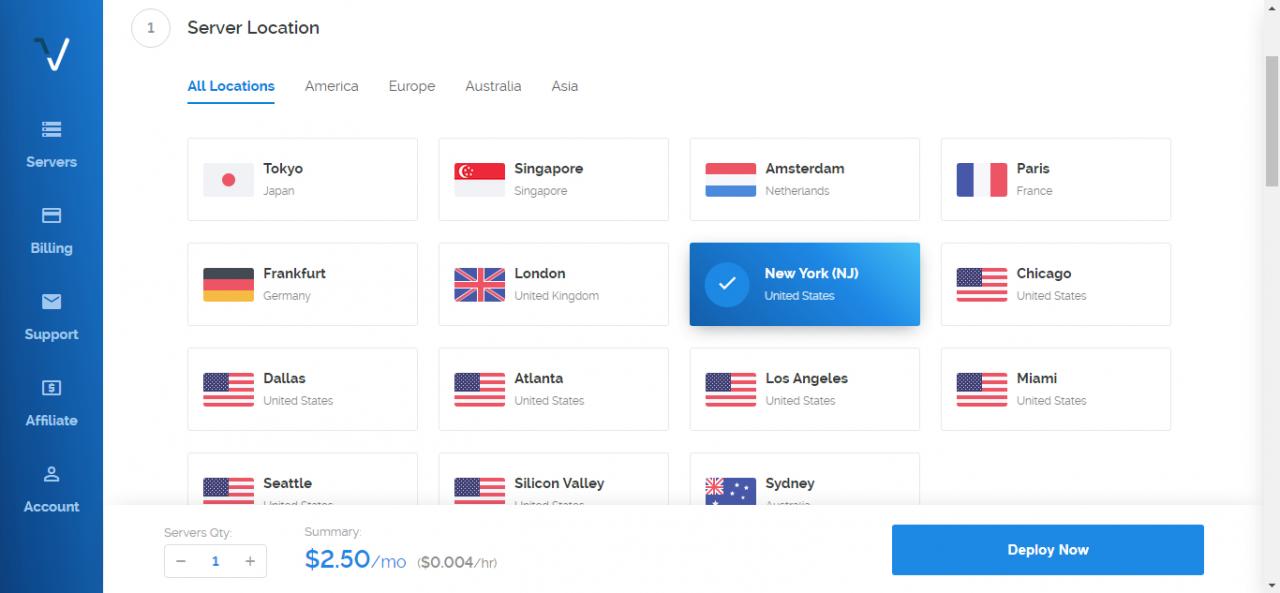
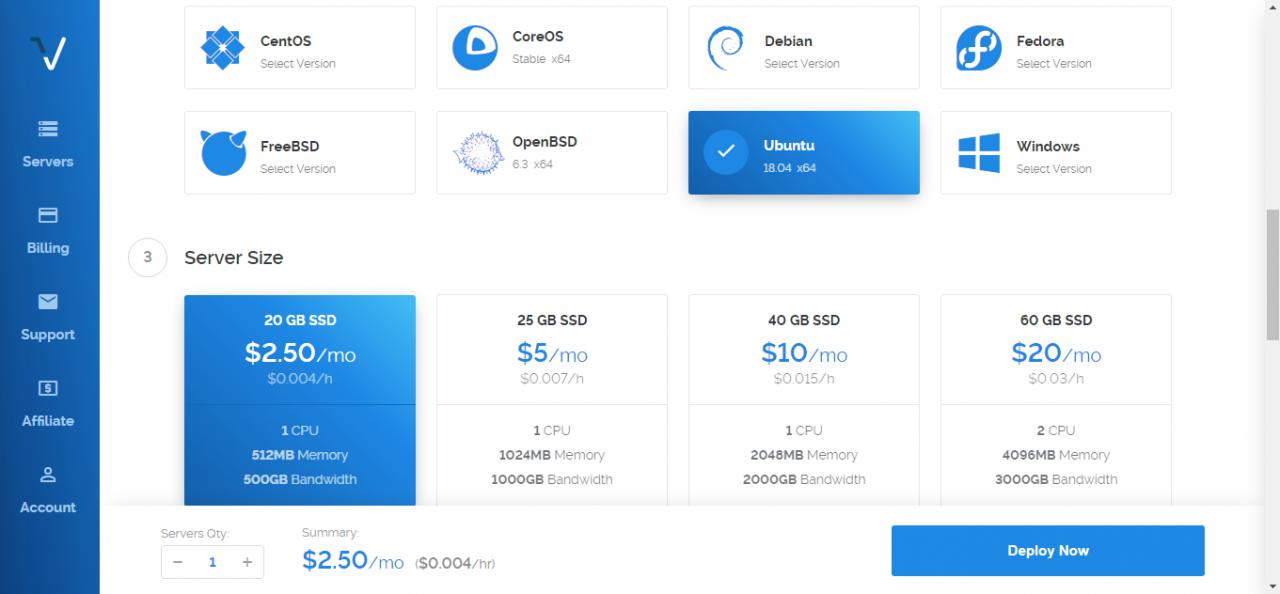
In this article, I will show you how to deploy BBR on a Vultr CentOS 7 KVM server instance.
Prerequisites
- A Vultr CentOS 7 x64 server instance.
- A sudo user.
Step 1: Upgrade the kernel using the ELRepo RPM repository
In order to use BBR, you need to upgrade the kernel of your CentOS 7 machine to 4.9.0. You can easily get that done using the ELRepo RPM repository.
Before the upgrade, you can take a look at the current kernel:
1 | uname -r |
This command should output a string which resembles:
1 | 3.10.0-514.2.2.el7.x86_64 |
As you see, the current kernel is 3.10.0.
Install the ELRepo repo:
1 | sudo rpm --import https://www.elrepo.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-elrepo.org |
Install the 4.9.0 kernel using the ELRepo repo:
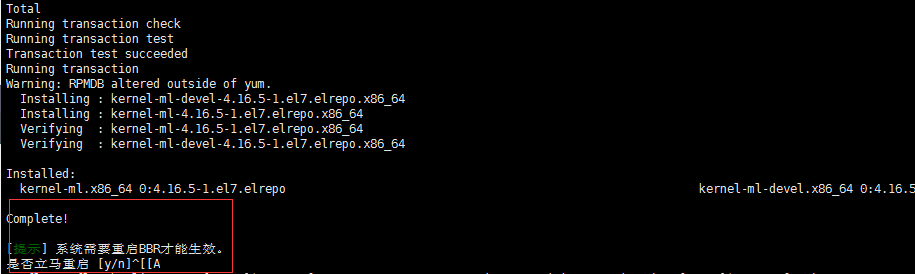
1 | sudo yum --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel install kernel-ml -y |
Confirm the result:
1 | rpm -qa grep kernel |
If the installation is successful, you should
see kernel-ml-4.9.0-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 among the output
list:
1 | kernel-ml-4.9.0-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 |
Now, you need to enable the 4.9.0 kernel by setting up the default grub2 boot entry.
Show all entries in the grub2 menu:
1 | sudo egrep ^menuentry /etc/grub2.cfg cut -f 2 -d \' |
The result should resemble:
1 | CentOS Linux 7 Rescue a0cbf86a6ef1416a8812657bb4f2b860 (4.9.0-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64) |
Indexing starts at 0. This means that the 4.9.0 kernel
is located at 1:
1 | sudo grub2-set-default ` |
Reboot the system:
1 | sudo shutdown -r now |
When the server is back online, log back in and rerun the uname command to confirm that you are using the correct Kernel:
1 | uname -r |
You should see the result as below:
1 | 4.9.0-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 |
Step 2: Enable BBR
In order to enable the BBR algorithm, you need to modify
the sysctl configuration as follows:
1 | echo 'net.core.default_qdisc=fq' sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf |
Now, you can use the following commands to confirm that BBR is enabled:
1 | sudo sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_control |
The output should resemble:
1 | net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_control = bbr cubic reno |
Next, verify with:
1 | sudo sysctl -n net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control |
The output should be:
1 | bbr |
Finally, check that the kernel module was loaded:
1 | lsmod grep bbr |
The output will be similar to:
1 | tcp_bbr 16384 0 |
Step 3 (optional): Test the network performance enhancement
In order to test BBR's network performance enhancement, you can create a file in the web server directory for download, and then test the download speed from a web browser on your desktop machine.
1 | sudo yum install httpd -y |
Finally, visit the
URL http://[your-server-IP]/500mb.zip from a web browser on
your desktop computer, and then evaluate download speed.
That's all. Thank you for reading.
copyright Vultr.com
版权归Vultr.com所有